How to use BO motor for School Project!
- Pihu Sehgal
- Aug 30, 2025
- 4 min read
While every parent’s dream is to see their kids excel in extracurricular activities, especially in technically evolving areas that is deemed useful in their future career prospects, many do struggle to make right choices of components for their School Projects.
Let’s learn about BO Motors Today – These are primary requirement of any mechanism for your kid’s first robotics projects.
What is BO Motor?
A BO Motor is a compact, lightweight, and low-cost DC motor, which is geared, commonly used in robotics and hobby projects. “BO” stands for Battery Operated because these motors are designed to run on small batteries (3-12V), making them perfect for simple or complex Robotics Projects.
Toy Motor vs BO Motor:
It is different from small toy motors (which are the simplest motors) which are not geared. Geared Mechanism in BO Motor enables them to run at fixed speeds (like 100 Revolution per Minute – RPM) and ensure the robot or mechanism is perfectly synced with the tasks it’s designed to perform.

There’s also another difference, Geared Motors typically offer more torque than Toy DC Motors, due to lower speed for same power (Remember 9th Grade Physics? Torque and Speed are inversely proportional) – This makes them more useful for applications that would need more load carrying capacity. It’s the same way car gearbox works! Wanna climb a steep road, well you will have to go to Lower Gear (that gives you Higher Gear Ratio).

How Motor Works:
An electric motor works by converting electrical energy into mechanical motion using the principles of electromagnetism. A current-carrying conductor within a magnetic field experiences a force, causing it to move. By arranging these conductors in coils and creating a rotating magnetic field from the stator, a force is generated on the rotor (the rotating part), which spins and produces the desired mechanical output. Refer to interactive video by Jared Owen.
Core Components found in typical DC motor:
Stator: The stationary part of the motor that contains permanent magnets.
Rotor: The part that spins, also containing coils of wire.
Brushes: Stationary contacts that deliver current from the battery to the rotating coils of wire.
Axle: The central shaft that transmits the rotor's mechanical power.

How BO Motor Works:
A BO Motor, or Battery Operated motor, is a DC motor with a built-in gearbox that uses Direct Current (DC) to operate. It works by taking electricity from a battery to spin the motor's rotor; the gearbox then reduces the high speed of the DC motor to a lower, more usable speed with increased torque, making it suitable for robots, toys, and other battery-powered projects.
A BO motor consists of a DC motor and a gearbox, which work together. Key components in a BO Motor includes:
DC Motor: This is the primary component that converts electrical energy into mechanical rotation.
Gearbox: Attached to the motor's shaft, the plastic gearbox contains a series of gears that reduce the motor's high rotational speed and increase its torque. For example, a motor with a 15:1 gear ratio means the internal motor spins 15 times for every one rotation of the output shaft, providing 15 times the torque. The gearbox provides several key advantages for hobbyist projects:
o High torque: The multiplied force allows the motor to drive heavier loads, such as a small robot's wheels.
o Controlled speed: The gear reduction significantly lowers the output speed, which makes it easier to control.
o Efficiency: The high torque at low speeds is well-suited for battery-powered projects, as it requires less energy to overcome resistance
Have a look at the video Gears Explained by The Engineering Mindset
Output shaft: The final shaft that provides the motion and is connected to wheels or other moving parts.
Plastic Housing (Yellow): A plastic casing, yellow color, that protects the internal components and provides mounting holes for easy installation
How to control BO Motor:
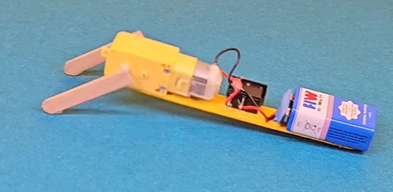
Direction: The direction of rotation is controlled by changing the polarity of the DC power input. Reversing the positive and negative wires will reverse the direction of the motor's spin. Refer to the illustrative image below.
Speed: The speed can be adjusted by changing the voltage of the DC power supply. For finer control, a motor driver or PWM controller can be used to rapidly switch the power on and off, effectively varying the average voltage and thus the speed.
Why BO Motors are popular choice for School Projects or beginners?
BO (Battery Operated) motors are popular for school projects because they are affordable, easy to use, and versatile, making them suitable for beginners and educational settings like robotics, IoT, DIY robots, and automation projects. Their low cost helps keep project budgets in check and addresses anxiety to failure, while their user-friendly nature and compact, low-power design make them perfect for hands-on learning and the development of small, self-contained projects.
Geared BO Motors (Battery Operated Motors) come very handy due to:
Safe for Kids: Runs at as low as 6-12V DC Power from Battery | No injury risks
Easy to Mount: Comes with Attractive Yellow Casing with holes to allow mounting screws
Versatile Product Range: Comes with multiple options like Single or Dual shaft and speed variations from 100 – 300 RPMs, based on inbuilt Gear-box.
Affordable: Very low cost compared to other specialized motors (Stepper / Servo)
Compact & Lightweight: Their small size and low weight make them ideal for small-scale projects where space and weight are constraints.
Energy Efficient: They are designed to run on small batteries (typically 3-12V), making them suitable for portable, self-powered applications that can run for longer time for a given battery.
High Torque for operation: The built-in plastic gearbox converts the motor's high speed into lower speed and higher torque. This added power is essential for driving the wheels of a small robot car or lifting a small load, while a regular DC motor might not have enough strength to do so. Also Gearbox helps to keep the speed of the shaft controlled.
With these features parents can select the appropriate motor for their kid’s School Project to boost up their confidence and get the stepping stone set for their future endeavours in Robotics.

Browse through TekBud’s catalogue to find the right fit for your kid’s projects.
Still confused or did not find the right fit for your kid’s project? Write to us and our experts shall be happy to guide you!
Here’s what other parents have to say about TekBud’s BO Motors:




Comments